The Historic Journey by Captain James Cook into the Antarctic Circle
Captain James Cook’s third and final voyage in the far south, beginning at the start of February 1774, marked a significant milestone in polar exploration. This expedition, crossing the Antarctic Circle, was notable for its venture into truly uncharted territories. As we commemorate the 250th anniversary of Captain James Cook’s 1773 Voyage to Antarctica, it’s crucial to understand its impact on our perception of discovery and exploration.
The Legacy of Explorers in Human History
Explorers have long held a place of high esteem in human history. Figures like Ferdinand Magellan, who debunked the myth of a flat Earth through his circumnavigation, and Marco Polo, who opened European eyes to the East, set the stage for Captain Cook’s exploration of the South Pole during his third voyage. Christopher Columbus‘s role in the discovery of the Americas cannot be overlooked either. These adventurers, through their quests for knowledge, riches, or new routes, inadvertently expanded our understanding of the natural world.
Captain Cook: Contributions to Maritime Discovery
Captain James Cook, a renowned British navigator during his first voyage, and explorer of the 18th century, is celebrated for reaching as far as the South Pole and significantly broadening our geographical knowledge. His exploration of the Antarctic Circle in 1773, spanning January 1773 to February 1774, stands as a testament to his determination and scientific curiosity. Captain Cook’s journey into the Antarctic on his second voyage marked a turning point in the history of exploration.
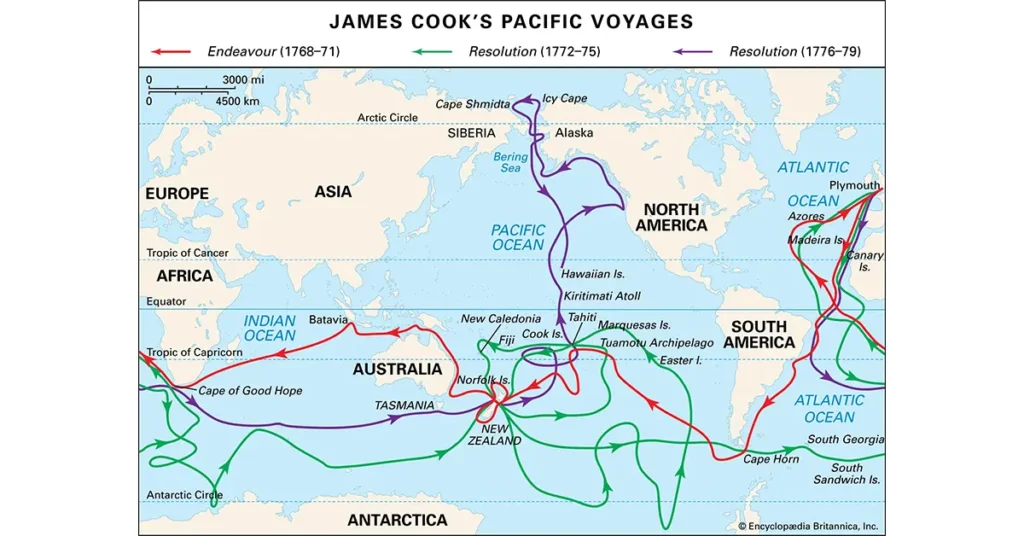
The Venture into the Unknown: A Second Voyage
Captain Cook’s Antarctic mission was part of his second voyage, which aimed to deploy exceptional navigation through the Southern Ocean and its surrounding lands. Setting sail from Plymouth on July 13, 1772, the expedition comprised two ships: the Resolution, under Cook’s command, and the Adventure, led by Captain Tobias Furneaux. The Royal Society and the Royal Navy organised Captain Cook’s second voyage with a focus on advancing our understanding of the Antarctic and the far south.
Disproving Terra Australis: A Major Achievement
One of Captain Cook’s significant accomplishments during his second voyage to Antarctica was disproving the existence of Terra Australis, a hypothesised massive southern continent. His meticulous charting of the icy waters and conclusion that no such landmass existed reshaped the world map and had profound implications for future exploration in the southern hemisphere.

Survival and Scientific Contributions in Harsh Conditions
Despite challenging conditions in Antarctica, Cook’s expedition exemplified resilience and exceptional navigation skills. The crew’s ability to survive the perils of the South Pole and Antarctic ice during their second voyage showcased their seamanship and Cook’s leadership. This voyage not only proved to be a feat of fortitude and courage but also yielded invaluable knowledge about the geography, climate, and ecosystems of the southern polar region. Cook’s detailed charts and records laid the foundation for future explorers and scientists to build upon.
Captain James Cook’s exploration of the far south, right up to the Antarctic Circle, is a pivotal chapter in the history of exploration, demonstrating the unyielding human spirit in the pursuit of knowledge and discovery.
Q: What was the significance of Captain James Cook’s 1773 expedition to the Antarctic Circle?
A: Captain James Cook’s 1773 expedition marked the first and only ship to cross the Antarctic Circle. It was undoubtedly the first significant exploration of the region.
Q: When did Captain James Cook cross the Antarctic Circle during his expedition?
A: Captain James Cook and his crew crossed the Antarctic Circle on 17 January 1773 during their historic voyage to Antarctica.
Q: What were the ships involved in Captain James Cook’s 1773 expedition?
A: The expedition was carried out using the two ships, Resolution and Adventure, commissioned by the Admiralty for the exploration of the Southern Hemisphere.
Q: What made Captain James Cook’s 1773 expedition an important milestone in the history of Antarctic exploration?
A: Cook’s voyages of discovery in the 1770s made it possible for man to reach the Antarctic Circle and provided valuable insights into the region’s geography and sea ice conditions.
Q: What obstacles did Captain James Cook face during his expeditions to the Antarctic Circle?
A: Cook and his crew encountered challenges such as navigating through sea ice, enduring harsh weather conditions, and the limitations of technology and knowledge about the region.
Q: Did Captain James Cook’s expeditions to the Antarctic Circle contribute to advancements in understanding longitude?
A: Yes, Cook’s voyages in the South Atlantic and Antarctic regions contributed significantly to advancements in understanding longitude and mapping the Great Southern Land.
Q: What were the outcomes of Captain James Cook’s 1773 expedition to the Antarctic Circle?
A: The expedition led to the exploration of new lands near the Antarctic Circle and provided valuable data for future Antarctic explorers and researchers.
Q: Did Captain James Cook’s expeditions have a lasting impact on the exploration of Antarctica?
A: Yes, Captain James Cook’s expeditions laid the groundwork for future Antarctic explorers and contributed to the understanding of the Terra Australis Incognita (unknown Southern Land).
Q: When did Captain James Cook return to England after his expeditions to the Antarctic Circle?
A: Captain James Cook returned to England in July 1775 after completing multiple voyages of discovery, including his significant Antarctic exploration in 1773.
Q: How is the 17th of January commemorated in relation to Captain James Cook’s expeditions?
A: The 17th of January is celebrated as the anniversary of Captain James Cook’s crossing of the Antarctic Circle during his historic 1773 expedition, a significant event in the history of Antarctic exploration.










